Research - (2023) Volume 18, Issue 4
Detection of Extended-Spectrum Ã-Lactamases (ESBLs), TEM, SHV and CTX-M genes among Staphylococcus haemolyticus isolates from cesarean section infections
Rabeea Abdul-Jaleel Ibrahim1, Mohammed A. Almazini2, Sad S. Mahdi Al-Amara3* and Amal Abdul-Imam Almazini4Received: 01-Dec-2023, Manuscript No. gpmp-23-122971; Editor assigned: 04-Dec-2023, Pre QC No. P-122971; Reviewed: 15-Dec-2023, QC No. Q-122971; Revised: 21-Dec-2023, Manuscript No. R-122971; Published: 29-Dec-2023
Abstract
Background: Cesarean section it regarded crucial risk factor for postpartum inflammatory because of uterine skin rapture, bladder catheterization, and endometritis. The S. haemolyticus is the second most recurrently pathogenic of clinical nosocomial infections, especially with sepsis, on skin and soft tissue infections mainly existing as abscess, paronychia, and serious infections in different the body systems.
Methods: One hundred and fifty swab samples were collected from women who had caesarean sections at Al-Basrah Teaching Hospital between October 2022 to January 2023. The Vitek®2 system test revealed for identify positive bacterial growth. Then double Disk Approximation Method (DAM) was used to tested S. haemolyticus isolates for produce Extended Spectrum β-Lactamase (ESBLs). For the β-lactamase gene amplification, three specific primers were employed: blaTEM, blaSHV and blaCTX-M genes.
Results: From October 2022 to January 2023, 150 swab samples were collected. The samples showed 57 (38%) positive bacterial growth, distributed 51(89. 5%) Gram-positive bacterial isolates, while 6(10. 5%) Gram-negative bacterial isolates, by Using the Vitek® 2 system, various bacterial species were identified, Staphylococcus haemolyticus the most predominant. Out of 34 isolates, 31 (91. 2%) were divided S. haemolyticus 39 (68. 42%) isolates, Staphylococcus aureus 6(10. 53%), Klebsiella spp. 4(7. 00%) isolates, Staphylococcus saprophyticus 3 (5. 30%) isolates, Escherichia coli 2 (3. 50%) isolates, Staphylococcus sciuri 1(1. 75%. ) isolate, Staphylococcus hominis 1(1. 75%) isolate, and Enterococcus faecium 1 (1. 75%) isolate. Out of (n=34) isolates that distributed to 31 (91. 2%) isolates were divided into S. haemolyticus 25 (74%), and S. aureus 6 (18%) isolates were gave positive results for producing extended-spectrum ß-lactamases (ESBLs). While, 3(8. 8%), isolates of S. haemolyticus were shown negative results for producing ESBLs by using of the double approximation method (DAM) The results of the current study revealed from (n=34) Staphylococci spp. were distributed to 28 (82%) S. haemolyticus and 6(18%), that 33(97. 1%) Staphylococcus spp. isolates gave positive results for the detection of TEM and SHV gene. While the 1(2. 9%) isolate was shown negative result for the detection of TEM, SHV and CTX-M genes. While in the present study the results showed that all 34 (100%) Staphylococcus spp. were gave positive results for detection of the CTX-M gene
Conclusion: The most isolates of S. haemolyticus and S. aureus were multi drug-resistant (MDR) were detected by using Vitek®2 compact system and most isolates of S. haemolyticus and S. aureus were producing extended-spectrum ß –lactamases(ESBLs).
Keywords
Cesarean section infections;Staphylococcus haemolyticus; ESBLs; TEM; SHV; CTX-M genes
Introduction
Cesarean section it regarded crucial risk factor for postpartum inflammatory because of uterine skin rapture, bladder catheterization, and endometritis [1,2]. The inappropriate antimicrobial agent, or prolonged used the antibiotics may lead to bacterial resistance and increased SSI rates [3,4]. S. haemolyticus it is considered one of the predominantly Coagulase Negative staphylococci (CONS). S. haemolyticus is non-motile, non-sporulation, Gram-positive and facultative anaerobic. However, the S. haemolyticus can be growth in optimal temperature between 30-40 ℃ with the presence of O2 and 10% of NaCl [5]. S. haemolyticus regard as inhabitants of the human and animal microorganisms, has been many reports as a relationship with nosocomial pathogens because biodiversity of microbial and virulence apparatus including resistance to antibiotics [6-8].
TheS. haemolytics is the second most recurrently pathogenic of clinical nosocomial infections, especially blood cultures of patients with sepsis, onskin and soft tissue infections mainly existing as abscess, paronychia, and serious infections in different the body systems involving endocarditis, meningitis, joint prosthetic infections, peritonitis, otitis media, urinary tract infections, septicemia and it is widespread in the hospital situation also on the hands of workers in the health care [9,10]. Furthermore, the increased of infectious associated with medical implanted and devices were caused by the pathogen interpreting Multi-Drug Resistant (MDR) Profiles [11,12]. Detect of ESBLs-producing organisms is critical for infection control and nosocomial outbreak prevention. The purpose of this study was detect Extended-Spectrum ß-Lactamases (ESBLs) genes TEM, SHV and CTX-M genes inS. haemolyticus isolates from cesarean section infections from Al-Basrah governorate, Iraq.
Materials and Methods
Collection of specimens
One hundred and fifty swab samples were collected from women underwent cesarean section for both emergency cesarean delivery, and elective cesarean delivery during period from Oct. 2022 to Jan. 2023 in Al -Basrah Teaching Hospital were selected depending on their medical history.
Isolation and identification
The samples were collected from patients underwent cesarean section. The swab samples were cultivated, the samples that gave positive results for bacterial growth identified by Vitek® 2 system.
Detection of Extended Spectrum β-Lactamase (ESBLs)
Double Disk Approximation Method (DAM)
The S. haemolyticus isolates was tested for produce Extended Spectrum β-Lactamase (ESBLs)by cultured on Mueller-Hinton agar plates, with disks of 20µg amoxicillin / 10µg clavulonic acid was placed in the center of the agar surface in center, (30 µg) cefotaxime, (30 µg) ceftriaxone, (30 µg) ceftazidime, and (30 µg) aztreonam arranged around it were approximately (20-30 mm center to center). The test was positive after an overnight incubation, with an enhanced zone of inhibition between disks [13].
Detection of ESBLs genes
Three specific primers that were used for the amplification of β-lactamase genes include: TEM, SHV and CTX-M genes Tab. 1.
| Primers | DNA Sequences | Length | Product Size bp | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| bla TEM | F: 5՝-CATTTCCGTGTCGCCCTTATTC- 3՝ | 22 | 800 bp | Perez, et al. [14] |
| R: 5՝-CGTTCATCCATAGTTGCCTGAC- 3՝ | 22 | |||
| blaSHV | F: 5՝- AGCCGCTTGAGCAAATTAAAC- 3՝ | 21 | 713 bp | Perez, et al. [14] |
| R: 5՝- ATCCCGCAGATAAATCACCAC- 3՝ | 21 | |||
| blaCTX-M | F: 5՝- CGCTGTTGTTAGGAAGTGTG- 3՝ | 20 | 754 bp | Ramachandran, et al. [15] |
| R: 5՝- GGCTGGGTGAAGTAAGTGAC- 3՝ | 20 |
Tab. 1. Specific primers used for detection of extended spectrum β-lactamase genes.
Results
From Oct. 2022 to Jan. 2023, 150 swab samples was collected from cesarean section patients at Al-Basrah Teaching Hospital were gave 57(38%) positive bacterial growth, 93(62%) negative for bacterial growth, and 51(89.5%) Gram -positive bacterial isolates, while 6(10.5%) Gram-negative bacterial isolates. As shown in Tab. 2.
| Total Number of Isolates | Gram +ve | Gram -ve | Percentage Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| 57 | 51(89.5%)* | 6(10.5%) | (100%) |
Tab. 2. Percentage of bacterial species isolated from cesarean section infections.
Identification of bacterial growth by using Vitek® 2 system have been emerged various bacterial species, the most predominant were S. haemolyticus, out of 57 bacterial isolates the 39(68. 42%) isolates, S. aureus 6(10.53%), Klebsiella spp 4(7.00%) isolates, Staphylococcus saprophyticus 3(5. 30%) isolates, E. coli 2 (3.50%) isolates, S. sciuri 1(1.75%) isolate, S. hominis 1(1.75%) isolate, and E. faecium 1(1.75%) isolate, as shown in Fig. 1.
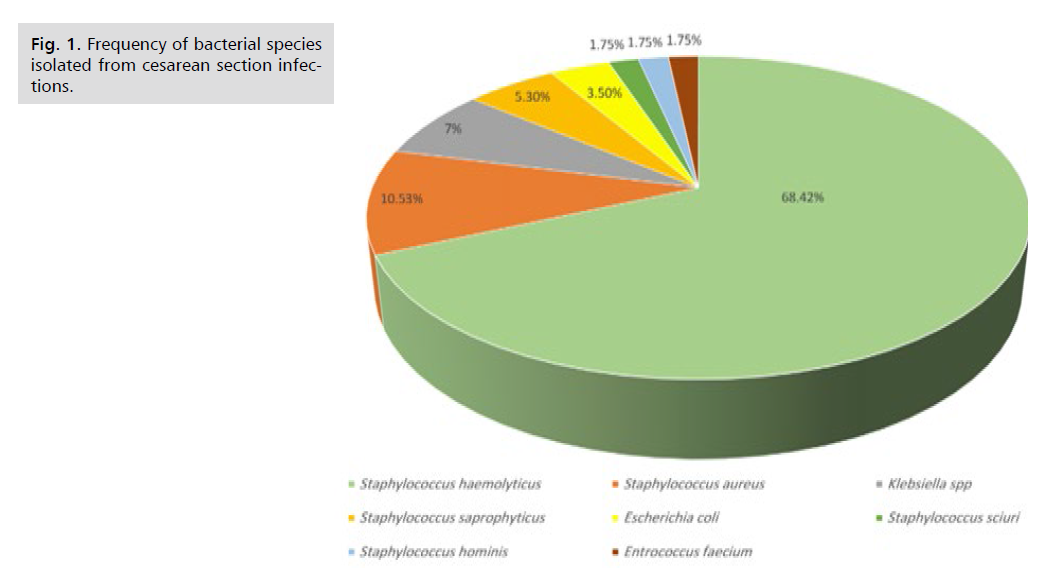
Fig. 1. Frequency of bacterial species isolated from cesarean section infections.
In present study emerged that out of (n=39) isolates were distributed to 28 (82%) S. haemolyticus isolates and 6(18%) S. aureus isolates was choice. The 25 (74%) S. haemolyticus isolates and S. aureus 6 (18%) isolates were gave positive results for producing extended-spectrum ß-lactamases (ESBLs). While, 3(8. 8%) S. haemolyticus isolates were shown negative results for producing ESBLs by using of the double approximation method (DAM), as shown in Fig. 2.
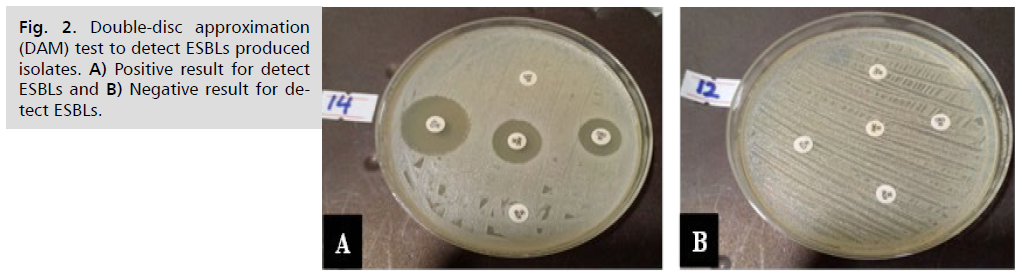
Fig. 2. Double-disc approximation (DAM) test to detect ESBLs produced isolates. A) Positive result for detect ESBLs and B) Negative result for detect ESBLs.
Also the results of the current study revealed out of 28(82%) S. haemolyticus isolates and 6(18%) S. aureus isolates the 33(97.1%) isolates gave positive results for the detection of TEM and SHV gene. While the 1(2.9%) isolate was shown negative result for the detection of TEM and SHV gene as shown in Fig. 3. and Fig. 4. While the results in present study were showed that all 34(100%) Staphylococcus spp.were gave positive results for detection of the CTX-M gene as shown in Fig. 5.
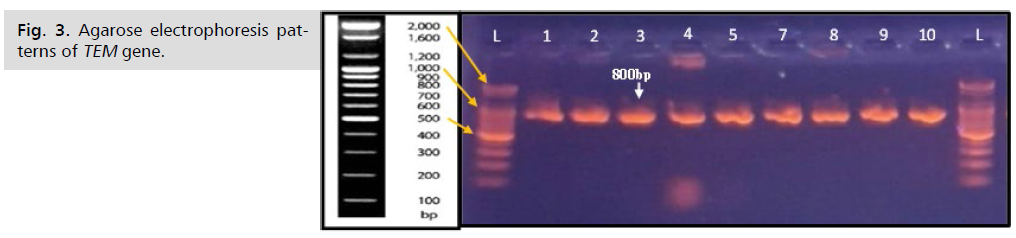
Fig. 3. Agarose electrophoresis patterns of TEM gene.
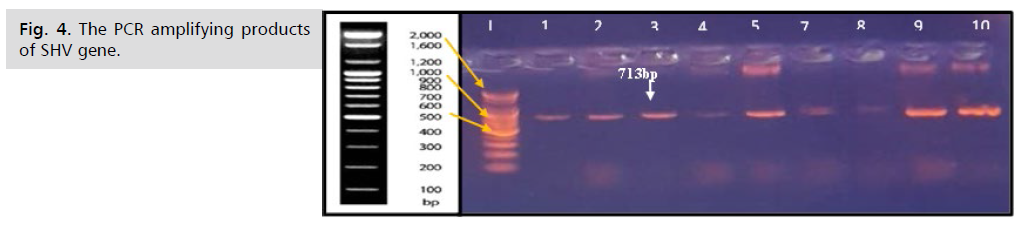
Fig. 4. The PCR amplifying products of SHV gene.
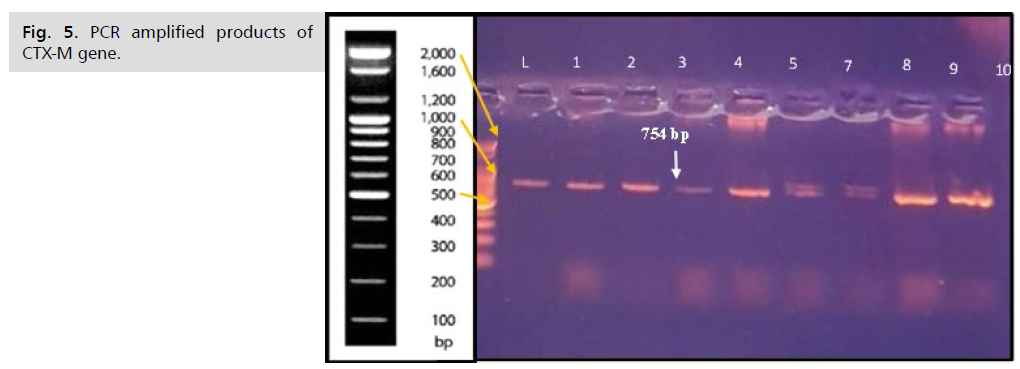
Fig. 5. PCR amplified products of CTX-M gene.
Discussion
The study found that Gram-positive bacteria isolates (89.5%) had a higher prevalence than Gram-negative bacteria (10.5%), contradicting previous studies that found a higher prevalence of Gram-negative bacteria (63.6%) and Gram-positive bacteria (36.4%) [14-16], these results are not compatible with this study. Whereas, another study results showed that (68. 4%) isolates Gram-negative bacteria and (31.6%) Gram-positive [17].
This variation could be attributed to environmental factors, geographical location, education level, and patients who took antibiotics before samples [18-20]. Factors such as hormonal changes, depression, menopause, hospital-acquired infections, immunocompromised patients, and long hospital stays can also contribute to the increased risk of infections [21-23]. Antibioticresistance genes are also a significantfactor [24-26].
The Vitek®2 system is an automated instrument designed for rapid and accurate identification of most staphylococci in clinical specimens [27-29]. It has been proven effective in detecting Gram-positive cocci and Gram-negative rods, with 99% accuracy and reproducibility confirmed by multiple independent studies [29]. The Colorimetric Vitek® 2 GP card is suitable for clinical samples, and has been praised for its performance in detecting Gram-positive and Gram-negative rods [30].
The results of the present study showed that (92%) isolates were gave positive result for producing extended-spectrum ß-lactamases, which agree with study by Hassuna, et al. [31] in Egypt that found (59. 7%) of their E. coli isolates were have ability to produce ESBLs. While the present study that disagreed with the study by Pandit, et al. [32] in Nepal which found that ESBLs production was at (40. 3%). Moreover, the results of other study revealed that (90%) isolates were produced ESBLs [33]. These results resembled with results.
The results of the present study showed that (97. 1%) isolates were gave positive result for TEM and SHV genes, this results which not agreement with study of Abdi, et al. [34] who reported (15%) of SHV gene. The results of the current study emerged that (97.1%) isolates were gave positive results for SHV gene, this results was compatible with study of Karimi, et al. [35] who reported that (82%) of isolates have this gene. This result was harmonious with study of Al–Ezee, et al. [36], were found (100%), but the study of Shahid, et al. [37] who were found (20%), and the study of Mahmoud, et al. [19] were found (17%), and the study of Alipour, et al. [38] who reported that absence of SHV gene.
The current study showed that (100%) isolates were gave positive results for CTX -M gene. While the results of other studies revealed that (77. 4%) isolates were CTX-M positive results [39]. On the other hand the results of other studies revealed that (43. 8%) isolates were gave positive result for CTX - M gene [40]. This result harmonious with study of Park, et al. [41]. Also bla CTX-M was found in another study of Maleki, et al. [42] who were found (92%) and [43] (100%). These results were compatible with present results.
Conclusion
The most isolates of S. haemolyticus and S. aureus were multi drug-resistant (MDR) were detected by using Vitek®2 compact system and most isolates of S. haemolyticus and S. aureus were producing extended-spectrum ß –lactamases (ESBLs).
Disclosure
None.
Funding
None.
Authors Contribution
(A) Study Design · (B) Data Collection . (C) Statistical Analysis · (D) Data Interpretation · (E) Manuscript Preparation · (F) Literature Search · (G) No Fund Collection
References
- van Dillen J, Zwart J, Schutte J, et al. Maternal sepsis: Epidemiology, etiology and outcome. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2010;23(3):249-254.
- Delamou A, Camara BS, Sidibé S, et al. Trends of and factors associated with cesarean section related surgical site infections in Guinea. J Public Health Afr. 2019;10(1).
- Zejnullahu VA, Isjanovska R, Sejfija Z, et al. Surgical site infections after cesarean sections at the University Clinical Center of Kosovo: Rates, microbiological profile and risk factors. BMC Infect Dis. 2019;19(1):1-9.
- Alfouzan W, Al Fadhli M, Abdo N, et al. Surgical site infection following cesarean section in a general hospital in Kuwait: Trends and risk factors. Epidemiol Infect. 2019;147:e287.
- De Vos P, Garrity GM. Bergey's manual of systematic bacteriology. Springer; 2009.
- Heilmann C, Ziebuhr W, Becker K. Are coagulase-negative staphylococci virulent?. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2019;25(9):1071-1080.
- Al-Tamimi M, Abu-Raideh J, Himsawi N, et al. Methicillin and vancomycin resistance in coagulase-negative Staphylococci isolated from the nostrils of hospitalized patients. J Infect Dev Ctries. 2020;14(01):28-35.
- Wolden R, Pain M, Karlsson R, et al. Identification of surface proteins in a clinical Staphylococcus haemolyticus isolate by bacterial surface shaving. BMC Microbiol. 2020;20(1):1-8.
- Silva PV, Cruz RS, Keim LS, et al. The antimicrobial susceptibility, biofilm formation and genotypic profiles of S. haemolyticus from bloodstream infections. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 2013;108:812-813.
- Eltwisy HO, Abdel-Fattah M, Elsisi AM, et al. Pathogenesis of S. haemolyticus on primary human skin fibroblast cells. Virulence. 2020;11(1):1142-1157.
- Pereira PM, Binatti VB, Sued BP, et al. Staphylococcus haemolyticus disseminated among neonates with bacteremia in a neonatal intensive care unit in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2014;78(1):85-92.
- Pereira-Ribeiro PM, Sued-Karam BR, Faria YV, et al. Influence of antibiotics on biofilm formation by different clones of nosocomial S. haemolyticus. Future Microbiol. 2018;14(9):789-799.
- Coelho NT, da Silva RS, Delmondes GM, et al. Occurrence of Extended-Spectrum Betalactamase (ESBL) and carbapenemases among ampicillin-resistant enterobacteriales recovered from a municipal raw sewage in Minas Gerais, Brazil. Rev Colomb Cienc Quim-Farm. 2021;50(3).
- Perez F, Hujer AM, Hujer KM, et al. Global challenge of multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007;51(10):3471-3484.
- Ramachandran A, Shanthi M, Sekar U. Detection of blaCTX-M extended spectrum beta-lactamase producing Salmonella enterica serotype Typhi in a tertiary care centre. J Clin Diagn Res. 2017;11(9):DC21.
- Kaplan NM, Smadi AA, Al Taani MI, et al. Microbiology of wound infection after caesarean section in a Jordanian hospital. East Mediterr Health J. 2003;9(5-6):1068-1074.
- Velin L, Umutesi G, Riviello R, et al. Surgical site infections and antimicrobial resistance after cesarean section delivery in rural Rwanda. Ann Glob Health. 2021;87(1).
- SA HH, Al-Amara SS, Shani WS. Frequencies of inducible clindamycin resistance in Methicillin-Re-sistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) isolates from tonsillitis in Al-Basrah governorate, Iraq. Appl Biochem Microbiol. 2023;59(S1):235-240.
- Mahmoud NE, Altayb HN, Gurashi RM. Detection of carbapenem-resistant genes in Escherichia coli isolated from drinking water in khartoum, Sudan. J Environ Public Health. 2020;2020.
- Ogefere HO, Omoregie R, Iriah SE. Urinary tract infection among cancer patients in Benin City, Nigeria. Int J Biomed Sci. 2021;7(3).
- Hardany MJ, Al-Abdullah AA, Al-Amara SS, et al. Molecular investigation of gram negative bacteria extended spectrum β-lactamase in haemodialysis patients in Basrah Province, Iraq. Plant Arch. 2020;20(1):1573-1576.
- Gaitonde S, Malik RD, Zimmern PE. Financial burden of recurrent urinary tract infections in women: A time-driven activity-based cost analysis. Urology. 2019;128:47-54.
- Ali SB, Perdawood D, Abdulrahman R, et al. Vitamin D deficiency as a risk factor for urinary tract infection in women at reproductive age. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2020;27(11):2942-2947.
- Al-Amara SS. Comparison between phenotype and molecular resistance characteristic in Staphylococcus epidermidis isolates from wound infections in Al-Basrah province, Iraq. Period Eng Nat Sci. 2021;9(2):897-903.
- Kukanur S, Meundi M, Bajaj A, et al. Co-relation between virulence factors and antibiotic resistance of E. coli, with special reference to uropathogenic E. coli. Medicine. 2015;17:32-36.
- Lindblom A, Kiszakiewicz C, Kristiansson E, et al. The impact of the ST131 clone on recurrent ESBL-producing E. coli urinary tract infection: A prospective comparative study. Sci Rep. 2022;12(1):10048.
- Funke G, Funke-Kissling P. Performance of the new VITEK 2 GP card for identification of medically relevant gram-positive cocci in a routine clinical laboratory. J Clin Microbiol. 2005;43(1):84-88.
- Layer F, Ghebremedhin B, Moder KA, et al. Comparative study using various methods for identification of Staphylococcus species in clinical specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 2006;44(8):2824-2830.
- Delmas J, Chacornac JP, Robin F, et al. Evaluation of the Vitek 2 system with a variety of Staphylococcus species. J Clin Microbiol. 2008;46(1):311-313.
- Nimer NA, Al-Saa'da RJ, Abuelaish O. Accuracy of the VITEK 2 system for a rapid and direct identification and susceptibility testing of gram-negative rods and gram-positive cocci in blood samples. East Mediterr Health J. 2016;22(3):193-200.
- Hassuna NA, Khairalla AS, Farahat EM, et al. Molecular characterization of Extended-spectrum ß-lactamase producing E. coli recovered from community-acquired urinary tract infections in Upper Egypt. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):1-8.
- Pandit R, Awal B, Shrestha SS, et al. Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase (ESBL) genotypes among multidrug-resistant uropathogenic E. coli clinical isolates from a teaching hospital of Nepal. Interdiscip Perspect Infect Dis. 2020;2020.
- Ramachandran G, Rajivgandhi GN, Chackaravarthi G, et al. Isolation and molecular identification of extended spectrum beta-lactamase producing bacteria from urinary tract infection. J Infect Public Health. 2021;14(12):1911-1916.
- Abdi S, Ranjbar R, Vala MH, et al. Frequency of bla TEM, bla SHV, bla CTX-M, and qnrA among E. coli isolated from urinary tract infection. Arch Clin Infect Dis. 2014;9(1).
- Karimi A, Rahbar M, Fallah F, et al. Detection of integron elements and gene groups encoding ESBLs and their prevalence in E. coli and Klebsiella isolated from urine samples by PCR method. Afr J Microbiol Res. 2012;6(8):1806-1809.
- Al–Ezee AS, Al–Taai HR, Sultan AA. Occurrence oh blaSHV, blaCTX-M, blaTEM and Integrons genes in coli Escherichia isolates from urinary tract infection. athesis. College of Education for pure science/Diyala University. 2019.
- Shahid M, Singhal M, Malik A, et al. ESBL Phenotypes And Prevalent Genotype Of Ctx-M Type Betalactamases In clinical isolates of E. coli In A North Indiantertiary Care Hospital. National Congress of Indian Association of Medical Microbiologists.
- Alipour M, Jafari A. Evaluation of the prevalence of blaSHV, blaTEM, and blaCTX Genes in E. coli isolated from urinary tract infections. Avicenna J Clin Microbiol Infect. 2019;6(3):83-87.
- Maina D, Revathi G, Whitelaw AC. Molecular characterization of multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae and E. coli harbouring extended spectrum beta-lactamases and carbapenemases genes at a tertiary hospital, Kenya. Microbiologia Medica. 2017;32(4).
- Castanheira M, Farrell SE, Deshpande LM, et al. Prevalence of β-lactamase-encoding genes among Enterobacteriaceae bacteremia isolates collected in 26 US hospitals: Report from the SENTRY Antimicrobial Surveillance Program (2010). Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013;57(7):3012-3020.
- Park Y, Kang HK, Bae IK, et al. Prevalence of the extended-spectrum beta-lactamase and qnr genes in clinical isolates of E. coli. Korean J Lab Med. 2009;29(3):218-223.
- Maleki N, Tahanasab Z, Mobasherizadeh S, et al. Prevalence of CTX-M and TEM β-lactamases in Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates from patients with urinary tract infection, Al-Zahra hospital, Isfahan, Iran. Adv Biomed Res. 2018;7.
- Founou RC, Founou LL, Allam M, et al. Whole genome sequencing of Extended Spectrum β-Lactamase (ESBL)-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae isolated from hospitalized patients in KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. Scientific Rep. 2019;9(1):6266.
Author Info
Rabeea Abdul-Jaleel Ibrahim1, Mohammed A. Almazini2, Sad S. Mahdi Al-Amara3* and Amal Abdul-Imam Almazini42Department of Biology, College of Science, University of Basrah, Basrah, Iraq
3Department of Pathological analyses, College of Science, University of Basrah, Basrah, Iraq
4Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Ministry of Health, Basrah Health Directorate, Al-Basrah Teaching Hospital, Basrah, Iraq
Copyright:This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.